SOLUBILITY PRODUCT: FORMULA, PRINCIPLES, AND APPLICATIONS OF SOLUBILITY PRODUCT
What is the Solubility Product?
When a less soluble solute is added to a solvent, an equilibrium is established between the undissolved solute (solid phase) and its solute part which completely dissociates into the ion.
AB(Solid) ⇌ AB (Soluble part) ⟶ A+ + B-
The product of the ionic concentration of the ions present in the saturated solution of an electrolyte at a given specific temperature is called solubility product or Ksp of a solution.
For more info, you can visit this site ChemED
Formula for Solubility Product
Ksp = Solubility Product Constant
A+ = cation in the solution
B- = anion in the solution
a,b = relative concentratin
Principles of Solubility Product
- If ionic product < solubility product: the solution remains unsaturated.
- If ionic product = solubility product: the solution remains saturated.
- If ionic product > solubility product: the precipitation of an electrolyte will occur.
Applications of Solubility Product
1. Precipitation of chloride of Group I metal cation ( Ag+).
The group I metal precipitated in the form of chloride when HCL is added in the salt solution because the solubility product of metal chloride is less than the ionic product.
2. Precipitation of sulphide of Group II metal cation (Cu++).
When the H2S gas is passed in the acidity salt solution. It dissociated as:
Due to the common ion H+, the concentration of S-- decrease. So, the group II metal cation precipitate in the term of sulphide because the solubility product of metal sulphide is less than the ionic product.
3. Precipitation of hydroxid3 of Group III A metal cation (Al++).
When NH4CL and NH4OH are added to the salt solution, they dissociated as:
Due to the common ion NH4+, the concentration of OH- decrease. So the group III-A metal cation precipitate in the form of hydroxide because the solubility product of metal hydroxide is less than the ionic product.
4. Precipitation of sulphide of Group III B metal cation (Ni++).
When H2S is passed in the salt solution by adding NH4OH and NH4CL, It dissociated as:
Due to the common ion NH4+, the concentration of OH- decrease. But the metal Hydroxide has a greater solubility product than the ionic product.
When H2S is passed, It dissociated as:
The OH- combine with h+ to form H2O. The concentration of H-- increas3 in such a way that the solubility product of metal sulphide is less than the ionic product.
5. Precipitation of carbonate of Group IV metal cation (Ca++).
When NH4OH, NH4CL and (NH4)2 CO3 are added to a salt solution, it dissociates as:
The Group IV metal cation precipitate in the form of carbonate because the sensitivity product of metal carbonate is less than the ionic product.
Thank You! for reading this SOLUBILITY PRODUCT: Formula, Principles and Applications of Solubility Product
If you really enjoyed reading then feel free to check our other blog:
If there are any other topics that you're confused about then you can suggest to us about it in the comment section so that we can clear your doubts easily and our next post might on that topic also.
Stay Safe, Stay Learning

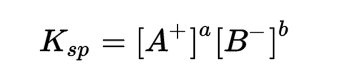
Comments
Post a Comment
Please, do not enter any spam links in the comment box.